ParameterTransfer¶
Overview¶
Revit Parameter Transfer is a NeroSync module designed to simplify transferring parameter values between Revit elements, families, and external Excel files. It is especially useful for BIM managers, coordinators, and designers who need to synchronize data quickly across multiple elements or families.
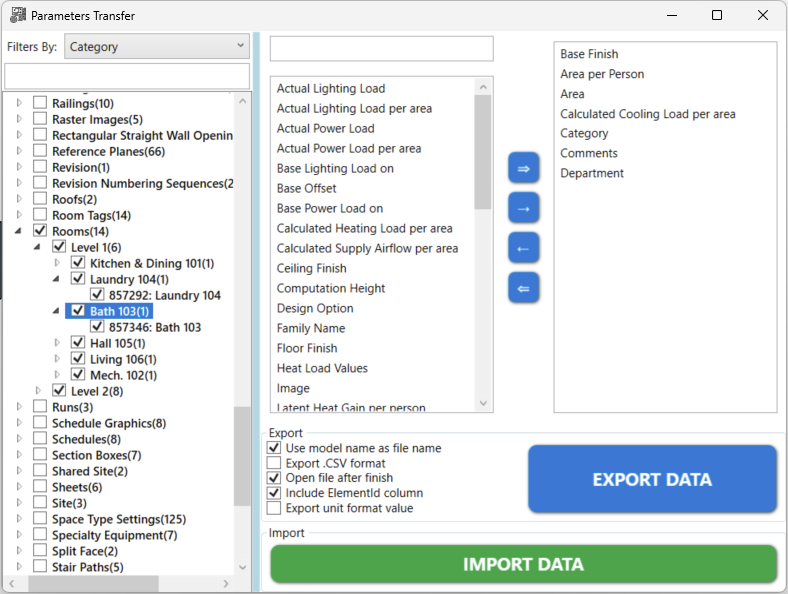
Features¶
- Export Revit parameters (instance and type) directly to Excel
- Edit in Excel and re-import values with high-speed processing
- Supports shared, project, and built-in parameters
- Clean, intuitive UI with element filtering and progress indicators
- Advanced element selection with deep filtering tree (category, family, type, view)
- Compatible with modern Revit versions (recommended: 2024 and newer)
- Ideal for data validation, QA/QC, and BIM coordination tasks
Use Cases¶
- Batch editing and updates of parameter values
- Coordinating with external stakeholders via Excel round‑trip
- Quality control and auditing of parameter data
- Querying data for reporting and analysis
- Model checking and validation
- Exporting data for external applications
Getting Started¶
Prerequisites¶
- Autodesk Revit (recommended 2024+)
- .NET Framework 4.8+
- Microsoft Excel (for editing exported data)
Installation¶
- Install NeroSync using your standard installer workflow.
- Launch Revit and open your project.
- Find “ParameterTransfer” under the NeroSync panel in the Add‑Ins tab.
Usage¶
- Open your Revit model.
- Navigate to Add‑Ins → NeroSync → ParameterTransfer.
- Choose Export Parameters or Import Parameters.
- For export, select categories and parameters, then export to Excel.
- Edit the Excel file as needed (retain headers).
- For import, load the modified Excel file, preview changes, and apply.
Workflow Details¶
Export Workflow¶
- Scope: choose categories, filters (e.g., level, phase, family/type), and parameters.
- Output: Excel file with stable headers (ElementId, Category, Family, Type, plus selected parameters).
- Tip: enable “include type parameters” if you intend to edit both instance and type values.
Import Workflow¶
- Load the edited Excel file.
- Map columns to parameters if headers were changed.
- Preview changes (diff view highlights changed values and conflicts).
- Apply changes using your chosen conflict policy: Overwrite, Skip, or Only Empty.
Configuration¶
- Save mapping presets to reuse common column→parameter bindings.
- Filters: limit scope by category, family, type, workset, or view.
- Units: choose unit handling (project units vs. raw values) to avoid conversion errors.
- Logging: enable change logs to export an audit CSV of applied updates.
Validation & Conflict Handling¶
- Read‑only parameters: flagged and skipped automatically.
- Type vs. instance parameters: type changes propagate to all instances of that type.
- Missing shared parameters: reported; provide guidance to add/bind before import.
- Unit types and formatting: incompatible units are highlighted in preview.
- Duplicate element rows: de‑duplicated by ElementId with last‑write‑wins (configurable).
Edge Cases & Limitations¶
- Linked models: parameters in links are read‑only unless opened directly.
- Grouped/arrayed elements: some parameters may be controlled by the group/array.
- Family parameters not exposed to instances cannot be edited at instance scope.
- Key schedules and calculated values may be read‑only.
Performance Tips¶
- Limit scope (categories and filters) to reduce data volume.
- Prefer presets for repeatable mappings; avoid manual re‑mapping each run.
- Test on a small selection, then scale to the full model.
- Close heavy views and disable graphics overrides to speed operations.
Best Practices¶
- Standardize parameter names using shared parameter definitions to avoid ambiguity.
- Keep a clean separation between type and instance parameters; avoid bulk changes to type values without review.
- Always back up or use a working copy before large imports.
- Use Excel data validation (lists, numeric ranges) to prevent invalid entries.
- Retain stable column headers (ElementId and parameter names) for reliable round‑trip.
- Export a change log and keep it with project documentation for auditability.
- Document and share mapping presets with the team to ensure consistency.
FAQ¶
- How are conflicts resolved? Use the preview to choose Overwrite, Skip, or Only Empty.
- Can I edit built‑in parameters? Many built‑in parameters are read‑only; the tool flags them.
- What if a parameter is missing? Add/bind the shared parameter first, then re‑import.
- Do units matter? Yes—choose project units or raw values consistently to avoid conversion issues.